China's aerospace industry is severely underestimated! The most important launch in the first half of 2023, you may not understand
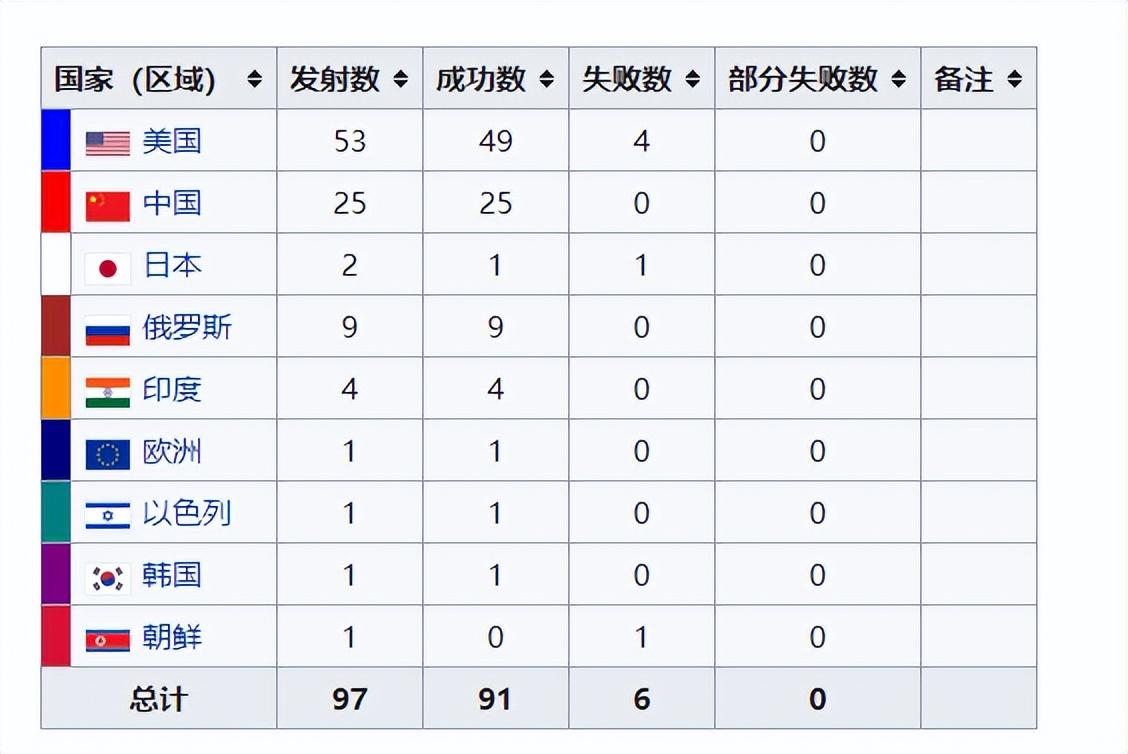
Half way through 2023, data on global space launches in the first half of the year has also been released.First place: United States, launched 53 times, succeeded 49 times, and failed 4 times;Second place: China, launched 25 times, all successful;Third place: Russia, launched 9 times, all successful;Fourth place: India, launched 4 times, all successful;Fifth place: Japan, launched twice, succeeded once, failed once;Sixth place: Europe, Israel, South Korea, launched once, all successful;Ninth place: North Korea, launched once, failed once
Half way through 2023, data on global space launches in the first half of the year has also been released.
First place: United States, launched 53 times, succeeded 49 times, and failed 4 times;
Second place: China, launched 25 times, all successful;
Third place: Russia, launched 9 times, all successful;
Fourth place: India, launched 4 times, all successful;
Fifth place: Japan, launched twice, succeeded once, failed once;
Sixth place: Europe, Israel, South Korea, launched once, all successful;
Ninth place: North Korea, launched once, failed once.
What are some noteworthy aspects of this?
1The US aerospace technology is entering the stage of "privatization";
Musk's SpaceX contributed 44 out of 53 launches in the United States, accounting for 83% of the total. Out of these 44 launches, it failed once.
The remaining portion of the United States adds up to 9 launches and 3 failures. Among them, "Virgin Orbit" launched once, "Relativity Space" launched once, and "ABL Space Systems" launched once. They all failed. "Rocket Lab" launched five times, all of which were successful. These four companies are actually private aerospace companies in the United States.

The "United Launch Alliance" successfully launched once. It appears to be a private aerospace company, but in fact it mainly deals with orders from the American League government and NASA, which can be regarded as a national team.
This means that in addition to the "United Launch Alliance", the rest of the United States is launched by private space companies. Of course, in fact, Rocket Lab will also make some orders from the US Department of Defense. In addition, NASA also awarded the super contract of "Lunar Lander" to "Blue Origin", the private aerospace company of Amazon founder Bezos, with the order value of $3.4 billion.
This means that NASA is transitioning from subcontracting to some companies with military backgrounds, gradually shifting to subcontracting to various private aerospace companies, includingThe reason why those enterprises were not useful in the past.

2. China's "national team+Private spaceflight" double track development;
China launched 25 times in the first half of the year, 19 of which were launched by national teams and 6 by Private spaceflight companies. The Bluebook of China Aerospace Science and Technology Activities (2022) released by China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation Co., Ltd. shows that,China plans to implement nearly 70 space launches throughout the year 2023.

This means that in the next six months, the national team will have 40 to 50 launch missions, which are very heavy, with an average of about 4 days, requiring only one launch. If Private spaceflight companies keep the trend of the first half of the year in the second half of the year, China is expected to achieve 70-80 launches in 2023, breaking the record of 64 launches in 2022.

3. The situation in other countries;
For 2022, Russia can only say that it is on par, with 22 launches throughout the year and 9 launches in the half year of 2023, which is still at its original level. And India's 2023 is quite good, with 5 launches and 4 successful launches in 2022. In the second half of 2023, it launched 4 successful launches and 4 successful launches, which has already caught up with last year. In terms of growth rate, India should be considered good. South Korea and Japan have both made some progress compared to last year, but the extent is not significant, while Europe has actually taken a step back.
4. What spacecraft are worth paying attention to?
Firstly, China made some technological breakthroughs in the first half of the year, especially the record of "multiple stars with one arrow", which was rewritten twice within a week.
Of course, it should be added that in 2023, the space station project is still going on in an orderly manner, and Human spaceflight is still going on, first Tianzhou 6, then Shenzhou 16, and the shift handover has been completed. Everything is going well. As last year, it does not mean that it is not noteworthy.

As for "multiple stars with one arrow", the previous record was "22 stars with one arrow" created by Long March 8 on February 27, 2022;
On June 7, 2023, China's largest solid-state rocket, the Lijian 1 Yao 2 carrier rocket, set a new record of 26 stars per rocket;
Just a week later, on June 15, 2023, China's "Long March 2 D" carrier rocket raised the record to "41 stars per arrow".

Of course, some people may want to say that based on the global record of "one arrow with multiple stars", India set a record of "104 stars per arrow" in 2017, while the latest record now is "143 stars per arrow" created by the US SpaceX Falcon 9 carrier rocket in 2021.
Is China's "multiple stars with one arrow" technology inferior to India?
Actually, that's not the case. "One arrow with multiple stars" is not just about quantity, but more importantly, quality. The so-called quality refers to the corresponding core technology.In summary, there are two items:
1
2. The separation technology between rockets and satellites.
Let's take the "One Arrow 104" created by India in 2017 as an example. At that time, the "PSLV-C37" polar Satellite Launch Vehicle was used, with a Low Earth orbit delivery capacity of 3.5 tons and a Sun-synchronous orbit delivery capacity of 1.75 tons. In contrast, China's "One Arrow 22 Satellite" uses the "Long March 8" carrier rocket, which has a Low Earth orbit delivery capability8.1 tons,The carrying capacity of Sun-synchronous orbit is not less than 4.5 tons, and its performance index is better than that of India's "PSLV-C37" polar Satellite Launch Vehicle. So why is India carrying more?
You probably guessed that the satellites carried by India are small in weight, with the main payload satellite "Cartosat-2D" weighing 730 kilograms, and the remaining 103 satellites, which add up to only 1.5 tons. Two satellites weigh 5-10 kilograms, while the remaining ones are all less than 5 kilograms, and even one kilogram. On the other hand, in China, the internal load of "One Arrow 22 Stars" (including brackets) is a total of 2.6 tons. So, in terms of rocket carrying capacity, India is not as good as China.

In addition, after sending these satellites up, it is necessary to achieve rocket and satellite separation. India adopts the simplest and most crude method, scattering all 104 satellites in one go and placing them in the same orbit. We are not saying that this operation is not feasible, but rather that this operation does not actually have a high technical levelIt will also increase the risk of collisions between satellites,The risk of collisions between rockets and satellites, especially after a long period of time, these satellites may also experience "collision" accidents.
In recent times, China has adopted various separation technologies for "multiple stars with one arrow". For example, the "One Arrow 26 Stars" created by the Lijian Yiyao 2 carrier rocket used various separation methods including memory alloy separation, initiating explosive device separation, and booster separation, successfully sending the satellite to different orbits.
The "One Arrow 41 Satellite" created by Chang Erding uses a different separation method, that is, the Retrorocket is used to reverse every time a batch of satellites is released, so that a sufficient safety distance can be reserved between the rocket and the satellite. This is:Layer by layer brake separation.

Therefore, China is actually ahead of India in terms of the delivery capacity of launch vehicles and the separation technology of rockets and satellites, which is also a leading level in the world. At present, China is only slightly behind SpaceX in the United States, but it also has its own unique Technology roadmap.
Many people may wonder, what is the importance of separation technology?
So the question arises, what if these rockets are not carrying satellites? What if it's carrying a warhead? Which technology has the advantage of spreading it all or spreading it in batches? In addition,Is it more advantageous to carry more ammunition at once?
By the way, China has just broken through the fourth generation explosive technology "CL-20" and lowered its price, making it lighter and more powerful. According to information disclosed by the US Department of Defense, many missiles in our country are equipped with this explosive, which means we can use less ammunition to achieve greater power. This also means that our missiles can actually be lighter and have stronger carrying capacity and warhead separation ability, so are these technologies useful? Is it a high judgment?

In addition to the technology of "one rocket with multiple satellites" and "space station and Human spaceflight", there is also a satellite worthy of attention in the first half of the year:Jilin-1This satellite is also jokingly referred to by military fans as an "agricultural satellite".
41Jilin-1
4136Jilin-15Jilin-1Jilin-1723610860138Jilin-1Jilin-1

So the question arises, why does a commercial project require our special attention?
You can roughly understand 'optical remote sensing' as:The Earth's selfie artifact.Jilin-1

Jilin-14K

Jilin-1
- After the completion of the first phase of construction, it will be able to achieve 24-hour, 24-hour, and full spectrum data acquisition, as well as 30 minute revisits at any location around the world;
- After the second phase of deployment is completed, it can achieve full day, 24/7, full spectrum data acquisition, and 10 minute revisits at any location around the world.
Jilin-1101381.33
Jilin-1
Jilin-1F-22

Jilin-1P-8A

Also, the US "Nimitz class nuclear powered aircraft carrier" was captured. It should be noted that during wartime, if an aircraft carrier is discovered, it means it will be destroyed. It's just very difficult to find an aircraft carrier in the vast sea. Previously, the Soviet Union reluctantly launched a large number of reconnaissance satellites to help Argentina confront Britain. In the end, these satellites had a very short lifespan and fell off in just over 10 days.

Jilin-1
500Jilin-1MF02A0410Gbps4010Gbps

What is this concept?
400-500MbpsJilin-11000Jilin-1Laser communication.
Jilin-1This is a commercial satellite,Jilin-1
Changchun Institute of Optics and Mechanics is not simple. It has participated in many national Megaproject, including the "two bombs and one satellite" project and the "Human spaceflight" project.
So, civilian ones are so strong, what are military ones like?
Anyway, I really don't know, and there have been no official reports. However, what I know is that on June 14, the US "Reagan" crossed the Bashi Channel and entered the South China Sea. The interesting scene came as a result,The Reagan suddenly realized that she was being watched,Five Chinese ships appeared around the Reagan, and in the following days, Chinese ships continued to "observe" the Reagan all the way until June 19th, when the Reagan left the South China Sea.

As the saying goes, it is not easy to discover the enemy's aircraft carrier. In wartime, once an aircraft carrier is discovered, it is basically equivalent to being destroyed. It is either a large number of anti-ship missiles or a large number of bombers carrying anti-ship missiles to greet it, with the main focus being a "dense attack" that keeps you from returning.
So the question arises, how was the Reagan discovered?
I don't know, I guess there should be ocean surveillance planes, military reconnaissance satellites, reconnaissance drones, and perhaps agricultural satellites, or a modified version of agricultural satellites?#What you see and what you get is very scientific # # Rocket # # Aerospace ##
Disclaimer: The content of this article is sourced from the internet. The copyright of the text, images, and other materials belongs to the original author. The platform reprints the materials for the purpose of conveying more information. The content of the article is for reference and learning only, and should not be used for commercial purposes. If it infringes on your legitimate rights and interests, please contact us promptly and we will handle it as soon as possible! We respect copyright and are committed to protecting it. Thank you for sharing.(Email:[email protected])















