Lettuce, scallions, and cherry tomatoes are growing well. The "Space Garden" has been upgraded and can be planted in rotation
CCTV News: As the manned mission of Shenzhou 17 approaches, the crew of Shenzhou 16 astronauts who are holding their positions on the Chinese space station are also about to complete their flight mission. The return is imminent, and the three astronauts continue to complete their tasks with high quality and quantity as planned, and actively engage in physical exercise to prepare for their return to Earth
CCTV News: As the manned mission of Shenzhou 17 approaches, the crew of Shenzhou 16 astronauts who are holding their positions on the Chinese space station are also about to complete their flight mission. The return is imminent, and the three astronauts continue to complete their tasks with high quality and quantity as planned, and actively engage in physical exercise to prepare for their return to Earth.
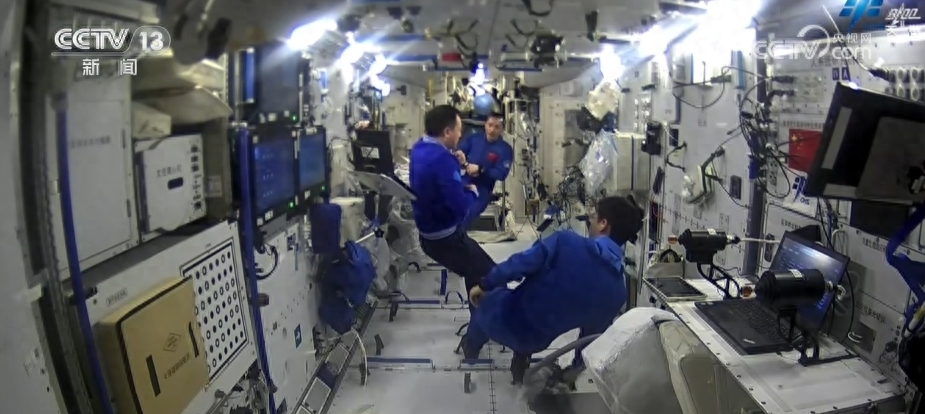



In addition to busy work, the "Space Vegetable Garden" has once again enjoyed a bountiful harvest. The astronauts picked and tasted the fresh vegetables they had grown in orbit. The space station has two space cultivation devices called "space vegetable gardens" in orbit, which grow lettuce, scallions, and cherry tomatoes, both of which are currently growing well.
The "Space Vegetable Garden" device used by astronauts to plant vegetables and fruits in space has been the second generation space plant cultivation device newly designed by the Chinese Astronaut Research and Training Center since the newly upgraded and reusable "Space Vegetable Garden" has entered the space station stage. They adopt a modular and open structure, which can better conduct plant cultivation experiments under orbital weightlessness conditions.

CCTV reporter Wang Xiaodan: This device in the space plant cultivation technology laboratory is the space cultivation device called "space vegetable garden", which is exactly the same as the cultivation device running in the space station, playing the role of "synchronization of heaven and earth" control experiment. The light, water, and nutrients required for plant growth can be scientifically and automatically configured here. Compared with the previous generation of space cultivation devices, its biggest feature is the ability to achieve rotation and multiple batches of cultivation, laying the foundation for future large-scale space cultivation.

Yang Runze from the Chinese Astronaut Research and Training Center: The lighting components adjust the frequency and illumination to the optimal plant lighting conditions by designing appropriate proportions of red, blue, and white light. This cultivation cup component provides a suitable root space for plant growth. This part similar to soil is called the substrate, and its initial state of ascent is dry and dry. Through the addition of water by astronauts in orbit, it becomes a state that is now suitable for plant growth.

CCTV reporter Wang Xiaodan: Can this substrate be recycled?

Yang Runze, Chinese Astronaut Research and Training Center: Yes. The inedible parts of a plant after growth can be crushed and compressed to regenerate a matrix block. These matrix blocks are then injected with water by astronauts to provide suitable growth space for it (the plant). At the same time, it also has some slow-release fertilizers in the middle, which provide some nutrients for plants, and the water supply components provide the same pure water that astronauts drink. We are currently conducting research on a new generation of plant cultivation techniques, which directly supply the water and nutrients needed by plants to their roots. At the same time, through some recycling and regeneration devices, these excess water and nutrients are recycled back, minimizing the waste of unusable parts as much as possible and increasing the proportion of recyclable materials.
Disclaimer: The content of this article is sourced from the internet. The copyright of the text, images, and other materials belongs to the original author. The platform reprints the materials for the purpose of conveying more information. The content of the article is for reference and learning only, and should not be used for commercial purposes. If it infringes on your legitimate rights and interests, please contact us promptly and we will handle it as soon as possible! We respect copyright and are committed to protecting it. Thank you for sharing.(Email:[email protected])