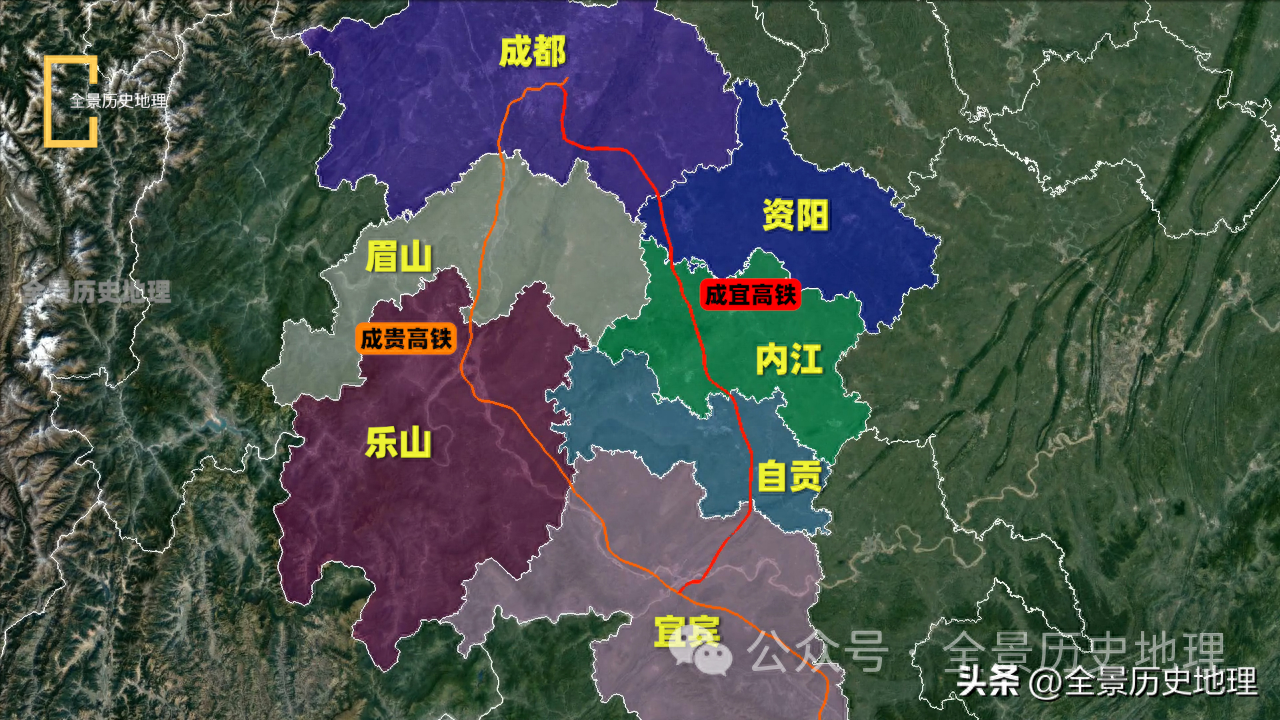
The persistence of ALG-125755 in mouse liver pharmacodynamics is associated with total siRNA and RISC binding siRNA
At the 2023 European Liver Conference (EASL 2023), researchers from the American clinical stage biopharmaceutical company AligosTherapeutics introduced another latest progress in the development of small interfering RNA (siRNA) ALG-125755 drugs,The pharmacodynamic persistence of ALG-125755 (a GalNAc binding siRNA) in mouse liver is related to the total siRNA and RNA inducible complex (RISC) binding siRNA.This study is sourced from Aligos Corporation, EASL2023The researchers introduced that the continuous disappearance of HBsAg (HBsAg) is required to achieve functional cure of chronic hepatitis B
At the 2023 European Liver Conference (EASL 2023), researchers from the American clinical stage biopharmaceutical company AligosTherapeutics introduced another latest progress in the development of small interfering RNA (siRNA) ALG-125755 drugs,The pharmacodynamic persistence of ALG-125755 (a GalNAc binding siRNA) in mouse liver is related to the total siRNA and RNA inducible complex (RISC) binding siRNA.

This study is sourced from Aligos Corporation, EASL2023
The researchers introduced that the continuous disappearance of HBsAg (HBsAg) is required to achieve functional cure of chronic hepatitis B. Targeted small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) have recently been clinically proven to significantly reduce HBsAg. ALG-125755 is a new type of N-Acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) binding siRNA, which is currently in clinical development stage.
This study demonstrated its mechanism of action, and in the therapeutic model of Adeno-associated virus (AAV) - HBV mice, it was associated with the persistent pharmacodynamics of total siRNA in mouse liver and siRNA combined with RNA induced silencing complex (RISC).
To confirm the mechanism of action of ALG-125755,The researchers used denatured polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to qualitatively measure the argonaute-2 (AGO-2) degradation of HBVRNA sequence in the target S region induced by antisense chain (AS) ALG-125736. In the previously reported efficacy study of Adeno-associated virus (AAV) - HBV mice, the total siRNA and RISC binding siRNA in the collected liver were quantified. The single administration of 10 mg/kg or repeated administration of 5 mg/mg every other week (Q2W) or every four weeks (Q4W) for 70 days showed a significant and lasting decrease in serum HBsAg.
The liver samples of the single dose group and the repeated dose group (14, 28, 70 days before administration, 98 and 168 days after administration) were analyzed by liquid chromatography with high resolution precision mass method to detect the total siRNA, and the RISC binding siRNA was detected by Immunoprecipitation/reverse transcription quantitative polymerase Chain reaction method.
ALG-125736, which is highly complementary to the S region of the HBV RNA sequence, can induce AGO-2 to cleave the target RNA sequence from the S region of HBV. The binding of ALG-125755 to AGO-2 protein was confirmed in both in vivo and in vitro in AAV-HBV mice. After a single administration in AAV-HBV mice, the half life of RISC binding siRNA (23.5 days) was twice that of the total siRNA in the liver (11.7 days).
After repeated administration of Q2W, the kinetics of RISC binding to siRNA were similar to that of total siRNA. After repeated administration, the concentration of RISC bound siRNA can remain stable. The siRNA binding to RISC can be quantified on the 168th day of the final study after repeated administration (Q2W regimen) and on the 98th day after a single administration.The persistence of HBsAg decrease is consistent with the total siRNA and RISC binding siRNA.
The results showed that the combination of ALG-125755 and AGO-2 was confirmed in vitro and in vivo models, and the mechanism of action of ALG-125755 was consistent with that of siRNA. In mouse liver, the pharmacological response and persistence of HBsAg reduction are associated with total siRNA and RISC binding siRNA. The half-life of RISC combined with siRNA is longer, indicating that the frequency of administration in the human body can be less than once a month.
Conclusion of Xiaofan Health: This study focuses on demonstrating that in the AAV-HBV mouse model, ALG-125755 has been confirmed to bind to argonaute-2 (AGO-2), and also confirms that the mechanism of action of ALG-125755 is consistent with that of small interfering RNA. The pharmacological response of HBsAg reduction and persistence is related to the total amount of siRNA in the mouse liver and the siRNA binding to RNA inducible complexes (RISCs). This study was presented by Professor KusumGupta from Aligos at this conference.
Disclaimer: The content of this article is sourced from the internet. The copyright of the text, images, and other materials belongs to the original author. The platform reprints the materials for the purpose of conveying more information. The content of the article is for reference and learning only, and should not be used for commercial purposes. If it infringes on your legitimate rights and interests, please contact us promptly and we will handle it as soon as possible! We respect copyright and are committed to protecting it. Thank you for sharing.(Email:[email protected])